该监测期涵盖了玉米和水稻的生长与收获阶段,以及大麦和小麦的播种阶段。7月至10月期间作物长势良好。
与平均水平相比,降水量略偏低2%,气温和光合有效辐射分别偏低0.3°C和3%,潜在生物量偏低1%。CropWatch农气指标接近过去15年平均水平。全国平均最佳植被状况指数为0.97,耕地种植比例显著增加12%,预示着夏粮产量向好。
如全国NDVI作物生长过程线图所示,7-8月作物长势接近平均水平,随后充沛的降水促使作物生长加速,达到并超过过去5年最佳水平,与降水时间过程线反映的一致。NDVI距平空间聚类图显示,监测期内月约7.2%的耕地区域作物长势始终低于平均水平,主要分布在河流沿岸,这与过量降水造成的河流沿岸作物受淹有关。此外,22.6%的耕地区域(集中于巴基斯坦北部,木尔坦北部和海得拉巴东部)作物长势在8月份之前不及平均水平,但9月份长势逐渐恢复至平均水平。复种指数达到146%,高于平均水平1%。
区域分析
为了更详细的进行空间分析,CropWatch基于地理和农业气候条件将巴基斯坦细分为三个农业生态区:印度河下游流域,北部高地和旁遮普邦北部地区。
在印度河下游流域,降水量显著偏高80%,气温和光合有效辐射分别低于平均值 0.1°C和3%,综合因素导致潜在生物量偏高4%。基于NDVI的作物生长过程线显示,7-8月作物长势低于平均水平,随后作物加速生长,长势超过近5年平均水平。耕地种植比例为66%,较2019年偏高15%,最佳植被状况指数为0.92, 表明作物长势总体优于近5年最佳水平。总体上,该地区的作物长势喜人。
北部高原地区的降水量偏高5%,光合有效辐射和气温分别减少5%和0.6°C,潜在生物量偏低10%。该地区的耕地种植比例相对较低,为65%,但仍显著高于过去5年平均水平(+12%)。基于NDVI的作物生长过程线显示,7-8月作物长势低于平均水平,随后逐渐恢复。总体而言,该地区的作物长势至少与平均水平持平。
巴基斯坦主要农业区北部旁遮普邦的降水量显著偏低21%。气温和光合有效辐射分别偏低0.2°C和2%,潜在生物量偏低18%。基于NDVI的作物生长过程线显示,7-8月作物长势低于平均水平,主要由于季风雨季推迟。此外,该地区的耕地种植比例为84%(比2019年偏高7%),最佳植被状况指数达到0.94。总体而言,该地区的作物长势看好。
图 3.23. 2020 年 7-10月巴基斯坦作物长势
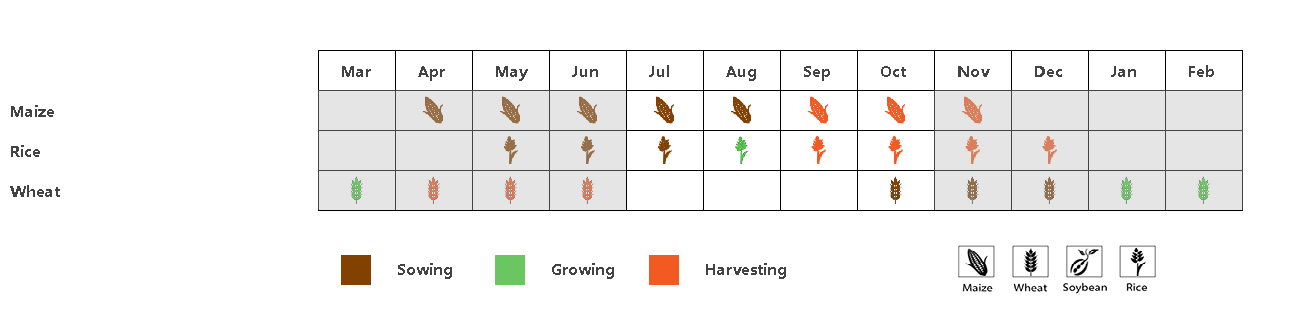
(a) 主要作物物候历
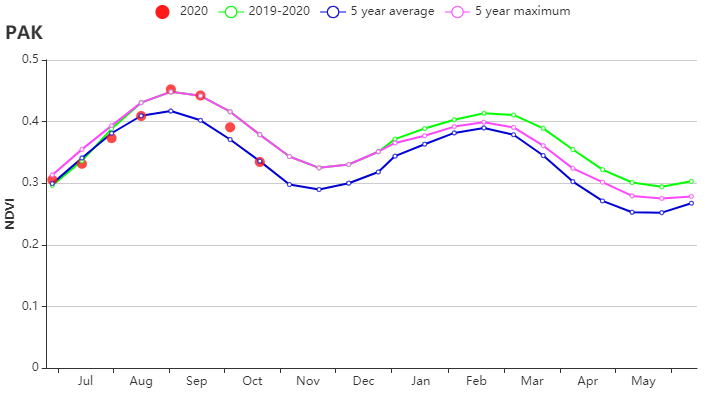
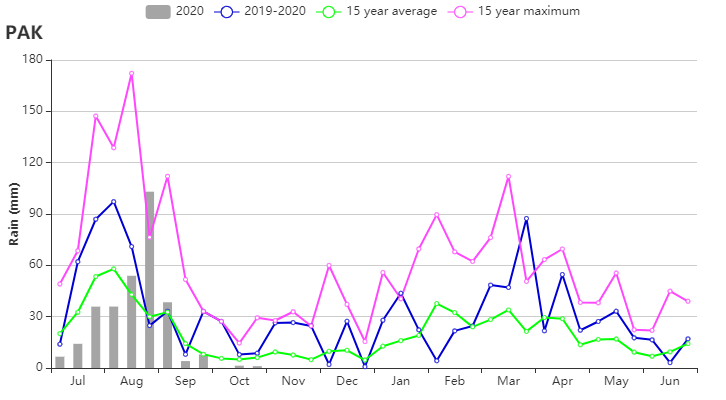
(b)基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线和降水时间过程线
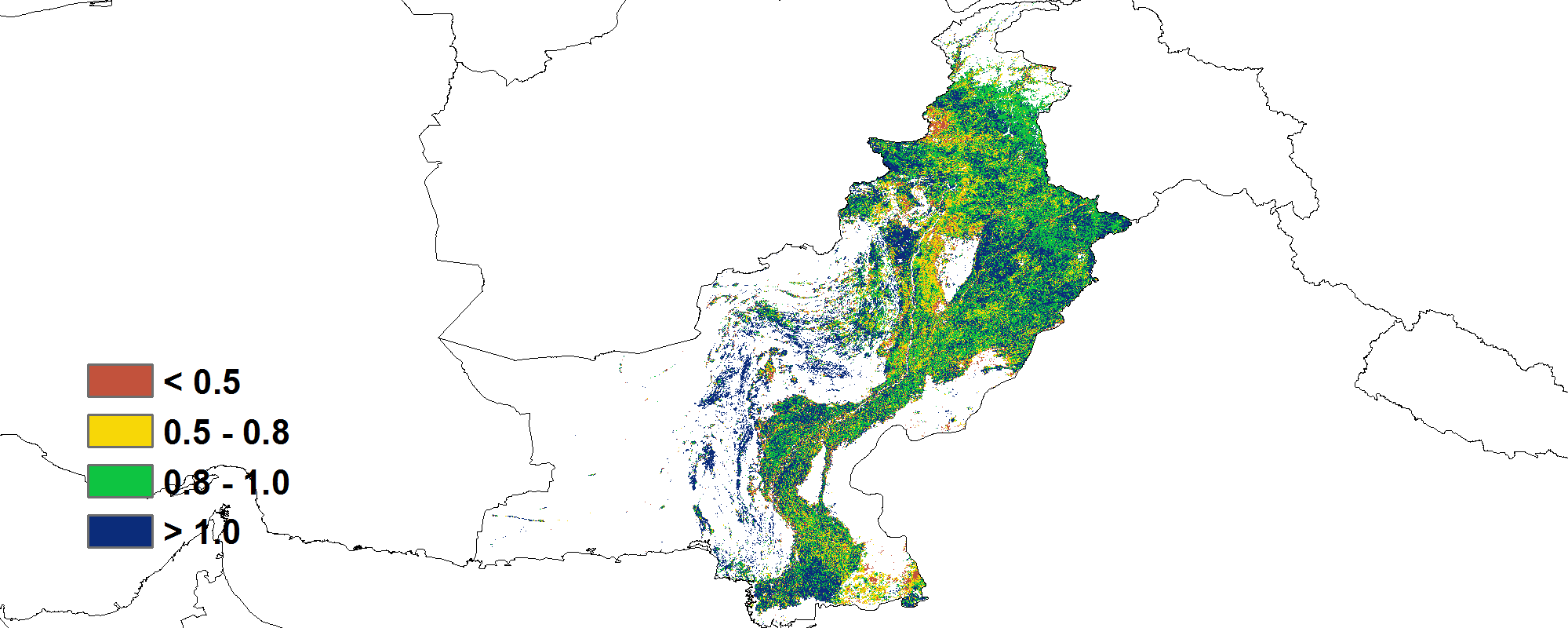
(c) 最佳植被状况指数

(d) 距平空间聚类图 (e) NDVI 距平聚类过程线
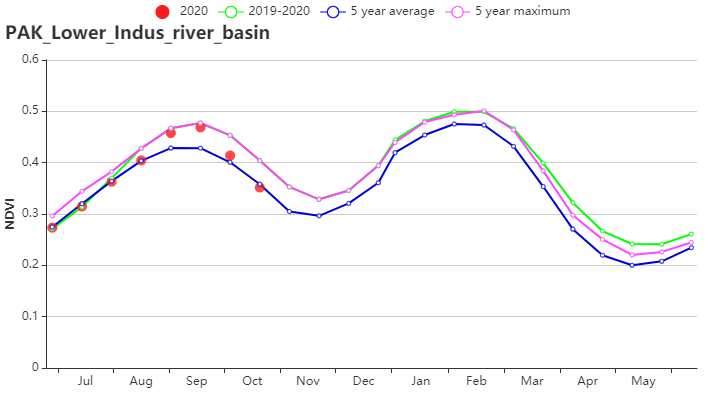
(f) 基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(印度河下游地区)
![]()
![]()
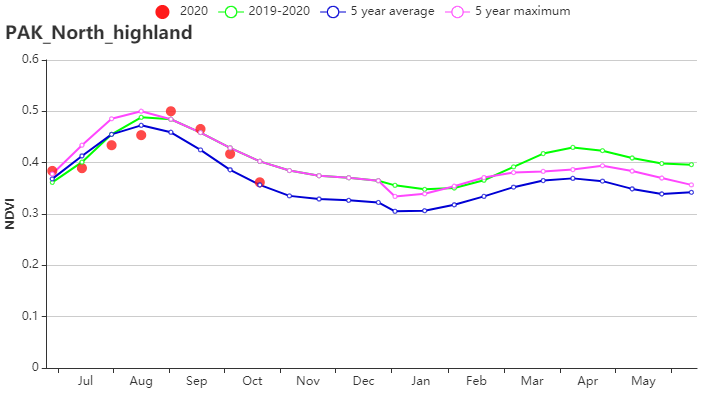
(g) 基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(北部山区)
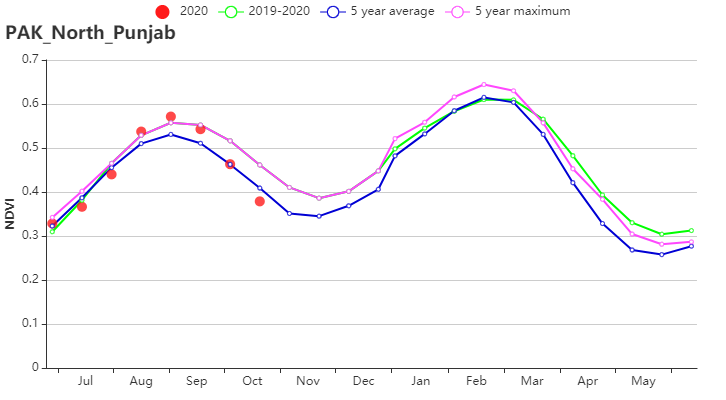
(h) 基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(北部旁遮普邦 )
表 3.56. 巴基斯坦农业生态分区 2020年 7 -10 月与过去 15 年(15YA)同期农业气象指标
分区 | 累计降水 | 平均气温 | 光合有效辐射 | 潜在生物量 | ||||
当前值(mm) | 距平(%) | 当前值 (°C) | 距平 (°C) | 当前值 (MJ/m2) | 距平 (%) | 当前值 (gDM/m2) | 距平(%) | |
印度下游流域 | 261 | 80 | 32.8 | -0.1 | 1265 | -4 | 591 | 2 |
北部山区 | 375 | 5 | 20.9 | -0.6 | 1309 | -5 | 537 | -10 |
北部旁遮普邦 | 281 | -21 | 30.7 | -0.2 | 1239 | -2 | 611 | -18 |
表3.57. 巴基斯坦农业生态分区 2020年 7 -10 月与过去 5 年(5YA)同期农情指标
分区 | 耕地种植比例 | 复种指数 | 最佳植被状况指数 | ||
当前值(%) | 距平 (%) | 当前值 (%) | 距平 (%) | 当前值 | |
印度下游流域 | 66 | 15 | 157 | 1 | 0.92 |
北部山区 | 65 | 12 | 132 | 3 | 0.95 |
北部旁遮普邦 | 84 | 7 | 177 | 3 | 0.94 |
