
Bulletin
wall bulletinMenu
- Overview
- Country analysis
- Afghanistan
- Angola
- Argentina
- Australia
- Bangladesh
- Belarus
- Brazil
- Canada
- Germany
- Egypt
- Ethiopia
- France
- United Kingdom
- Hungary
- Indonesia
- India
- Iran
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Cambodia
- Sri Lanka
- Morocco
- Mexico
- Myanmar
- Mongolia
- Mozambique
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Poland
- Romania
- Russia
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United States
- Uzbekistan
- Viet Nam
- South Africa
- Zambia
- Kyrgyzstan
Authors: 超级管理员 | Edit: liuwenjun
Late rice completed its complete cycle from sowing to harvesting in southern China during the monitoring period. The condition of the crop was generally close to but below average, according to the NDVI development curves.
Regionally, rainfall reached 1172 mm, which was 2% lower than the average; provincial departures were the following: +4% in Guangdong, +3% in Yunnan, -5% in Fujian, and +5% in Guangxi. In Guangdong and Guangxi, RAIN exceeded 1100 mm, while in Yunnan and Fujian it exceeded 900 mm.
The average temperature during the monitoring period in South China was 22.3 ° C, which was above average by 0.2° C. BIOMSS was 2% higher than average. The biomass index of Fujian, Guangdong and Yunnan increased by 8%, 1% and 8%, respectively, while Guangxi recorded a 3% drop. At the provincial level, biomass changes are consistent with sunlight (RADPAR), which is the dominant limiting factor for crop growth when water supply is sufficient. The average VCIx of the South China region during the monitoring period was 0.90, and almost all regions presented above 0.80 VCIx during this monitoring period.
NDVI departure clustering analysis revealed the continous below average condition crops were mostly located in south-western Guangdong Province, covering 17.2% of the total cropland area. Overall, the crops in Southern China was slightly below average.
Figure 4.13. Crop condition Southern China region, July-October 2019
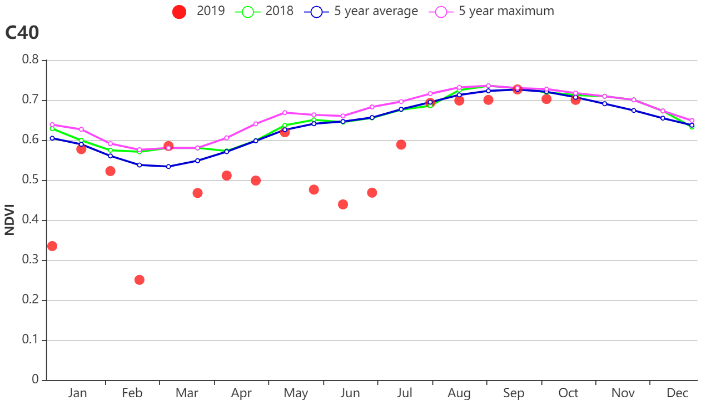
(a) Crop condition development graph based on NDVI

(b) Rainfall profile
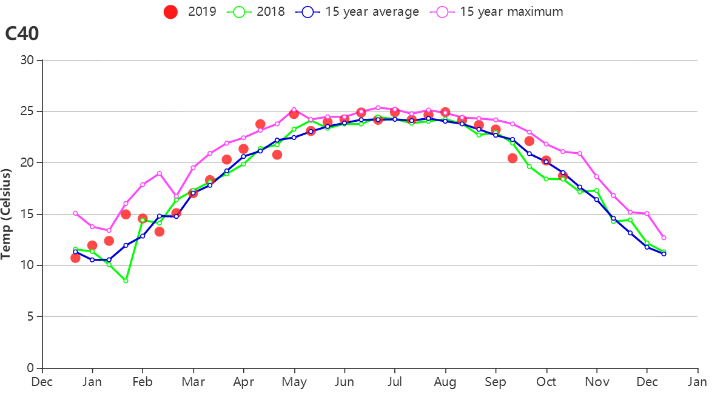
(c) Temperature profile
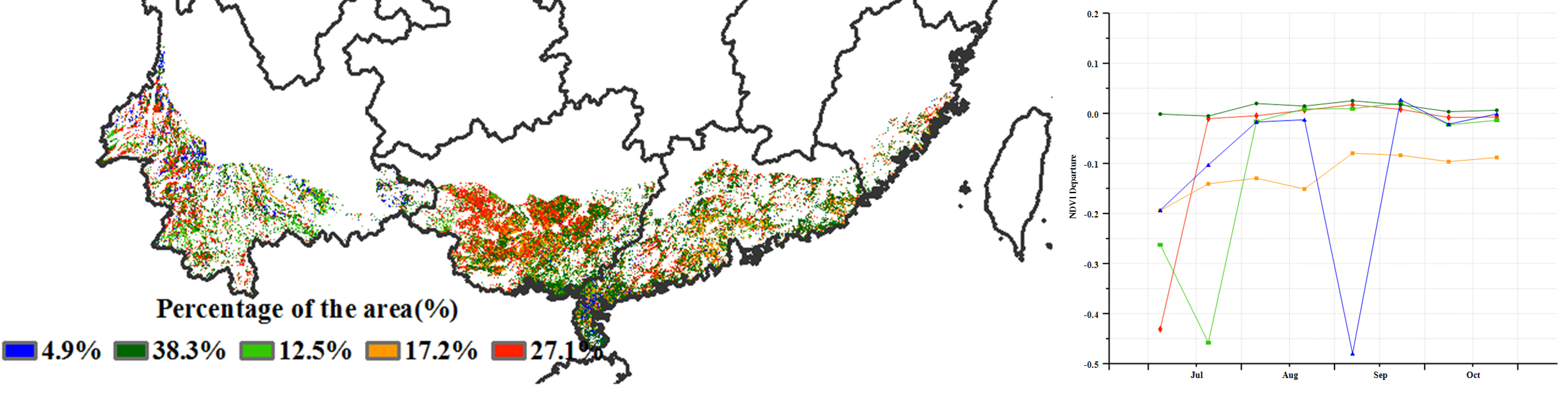
(d) Spatial NDVI patterns compared to 5YA (e) NDVI profiles

(f) Maximum VCI

(g) Biomass
